Ethylene Oxide Sterilization Service
Why Ethylene Oxide?
Ethylene oxide (EO) is the most commonly used agent in chemical sterilization. Because it is a gas, it rapidly penetrates packaging and items to be sterilized at temperatures tolerated by almost all materials. Ethylene oxide is an alkylating agent that kills microorganisms by inactivation of proteins, DNA, and RNA, and it is effective against vegetative bacteria, fungi, viruses, and spores. Because ethylene oxide penetrates materials more readily than steam, a wider variety of materials may be used in packaging items for sterilization and storage. Films of polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride are penetrated effectively by ethylene oxide.
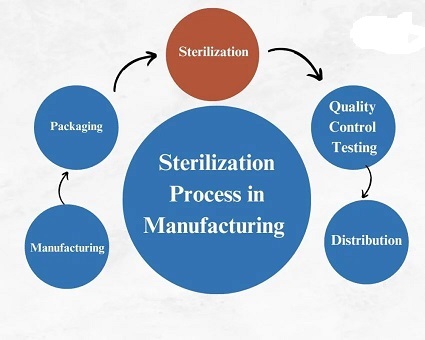
sterilization and much more economical than gamma sterilization. It is the recommended sterilization choice
to be used in all medical equipment and instruments that are sensitive to heat and humidity.
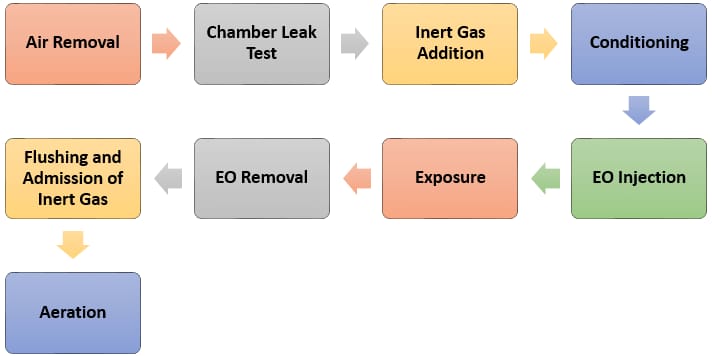
Equipped for your Sterilization Needs
The ETO sterilization process uses a colorless gas, ethylene oxide (EO) to sterilize various medical devices. This process has three segments i.e. Preconditioning, Chamber & Aeration. ETO is a very efficient process for the sterilization of medical devices. During the preconditioning stage, air is removed to allow the gas to enter the chamber, and within the chamber; the rotary pumps are designed such that they maintain an optimum ETO concentration. The chamber is heated by steam which ensures that the sterilizer is completely airless. ETO sterilization process can be customized for various medical devices and is particularly apt for parts that cannot withstand the high temperatures and humidity of autoclave sterilization. ETO is also well-suited for medical devices with embedded electronics as the temperature conditions are maximum up to 60° C / 140°F.